这一篇文章介绍了restframework中的request和response,主要是用来前端页面和后端进行交互。
中文文档:https://q1mi.github.io/Django-REST-framework-documentation/tutorial/2-requests-and-responses_zh/
双R
Request
- rest_framework.request
- 将Django中的request作为了自己的一个属性_request
- Response
APIView
之前我们在views.py中继承的View都是Django自带的原生View,现在我们使用restframework的视图类:APIView
验证:
class StudentView(APIView): # 这时继承restframework中的APIView
def post(self,request):
print(type(request))
return JsonResponse({'msg':'ok'})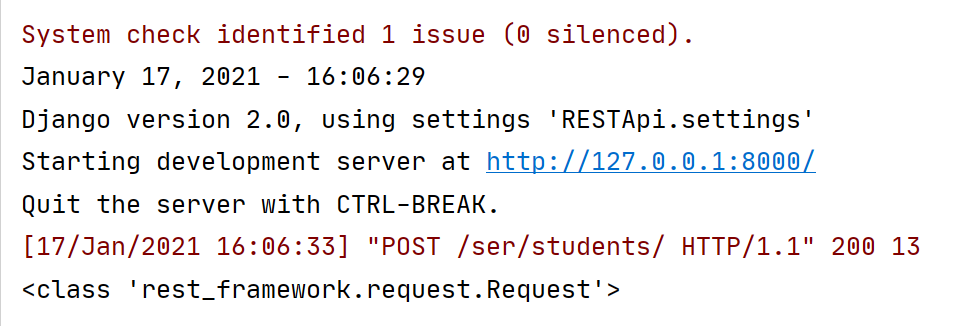

查看APIView的源码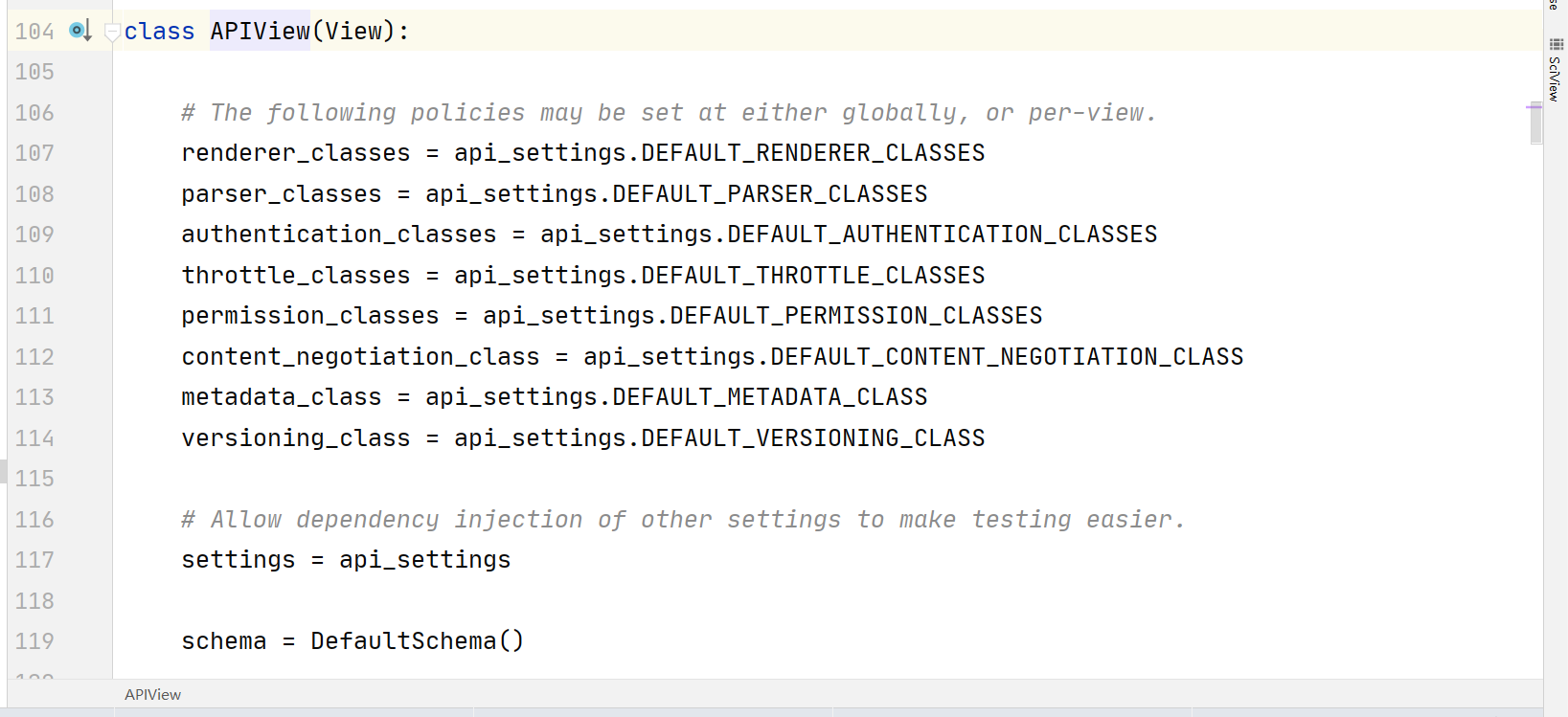

可以看到APIView继承自Django原生view,同时它还添加了很多限制条件,如107-114行。
这些限制条件类似于中间件,restframework框架都封装好,直接调用即可
policy,译为政策,一般是预设的一种限制条件,举个例子
renderer_calsses
- 渲染的类
paeser_classes
- 解析转换的类
authentication_classes
- 认证的类
throttle_classes
- 节流的类
控制请求频率的类
- 例如控制接口每分钟只能请求10次,超过次数禁止请求,之前是亲手写中间件去实现
permission_classes
- 权限的类
content_negotitation_class
- 内容过滤类
mdetadata_class
- 元信息的类,必须满足某种元信息才能使用
versioning_class
- 版本控制的类
api_settings
以上的限制都是来自于api_settings,查看api_settings源码
api_settings = APISettings(None, DEFAULTS, IMPORT_STRINGS)
def reload_api_settings(*args, **kwargs): # 这个是用于我们调整完设置之后,全局加载设置
setting = kwargs['setting']
if setting == 'REST_FRAMEWORK':
api_settings.reload()继续查看APIsettings: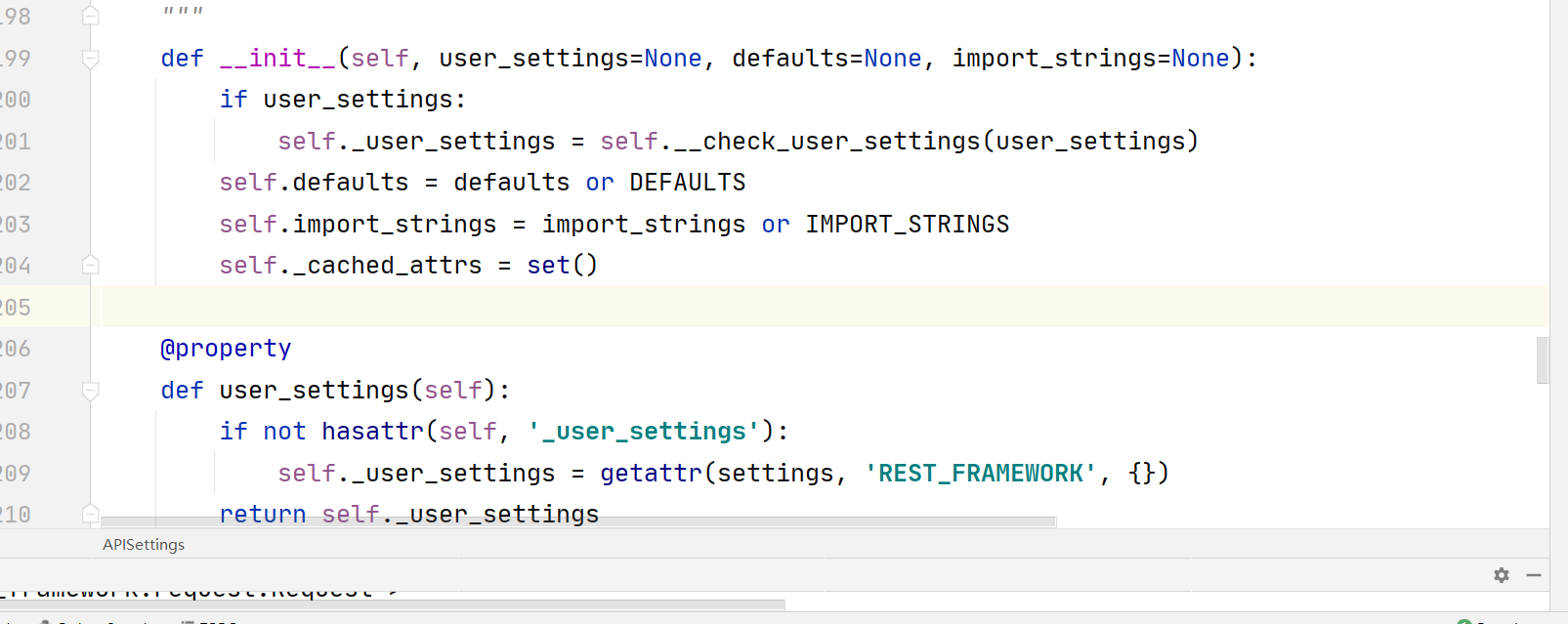

可以看到该类初始化时有三个参数: user_settings,defaults,import_strings
DEFAULTS
之前我们都是默认使用defaults参数,点击查看defaults参数内容:
DEFAULTS = {
# Base API policies
'DEFAULT_RENDERER_CLASSES': [
'rest_framework.renderers.JSONRenderer',
'rest_framework.renderers.BrowsableAPIRenderer',
],
'DEFAULT_PARSER_CLASSES': [
'rest_framework.parsers.JSONParser',
'rest_framework.parsers.FormParser',
'rest_framework.parsers.MultiPartParser'
],
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': [
'rest_framework.authentication.SessionAuthentication',
'rest_framework.authentication.BasicAuthentication'
],
'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES': [
'rest_framework.permissions.AllowAny',
],
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES': [],
'DEFAULT_CONTENT_NEGOTIATION_CLASS': 'rest_framework.negotiation.DefaultContentNegotiation',
'DEFAULT_METADATA_CLASS': 'rest_framework.metadata.SimpleMetadata',
'DEFAULT_VERSIONING_CLASS': None,
# Generic view behavior
'DEFAULT_PAGINATION_CLASS': None,
'DEFAULT_FILTER_BACKENDS': [],
# Schema
'DEFAULT_SCHEMA_CLASS': 'rest_framework.schemas.openapi.AutoSchema',
# Throttling
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES': {
'user': None,
'anon': None,
},
'NUM_PROXIES': None,
# Pagination
'PAGE_SIZE': None,
# Filtering
'SEARCH_PARAM': 'search',
'ORDERING_PARAM': 'ordering',
# Versioning
'DEFAULT_VERSION': None,
'ALLOWED_VERSIONS': None,
'VERSION_PARAM': 'version',
# Authentication
'UNAUTHENTICATED_USER': 'django.contrib.auth.models.AnonymousUser',
'UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN': None,
# View configuration
'VIEW_NAME_FUNCTION': 'rest_framework.views.get_view_name',
'VIEW_DESCRIPTION_FUNCTION': 'rest_framework.views.get_view_description',
# Exception handling
'EXCEPTION_HANDLER': 'rest_framework.views.exception_handler',
'NON_FIELD_ERRORS_KEY': 'non_field_errors',
# Testing
'TEST_REQUEST_RENDERER_CLASSES': [
'rest_framework.renderers.MultiPartRenderer',
'rest_framework.renderers.JSONRenderer'
],
'TEST_REQUEST_DEFAULT_FORMAT': 'multipart',
# Hyperlink settings
'URL_FORMAT_OVERRIDE': 'format',
'FORMAT_SUFFIX_KWARG': 'format',
'URL_FIELD_NAME': 'url',
# Input and output formats
'DATE_FORMAT': ISO_8601,
'DATE_INPUT_FORMATS': [ISO_8601],
'DATETIME_FORMAT': ISO_8601,
'DATETIME_INPUT_FORMATS': [ISO_8601],
'TIME_FORMAT': ISO_8601,
'TIME_INPUT_FORMATS': [ISO_8601],
# Encoding
'UNICODE_JSON': True,
'COMPACT_JSON': True,
'STRICT_JSON': True,
'COERCE_DECIMAL_TO_STRING': True,
'UPLOADED_FILES_USE_URL': True,
# Browseable API
'HTML_SELECT_CUTOFF': 1000,
'HTML_SELECT_CUTOFF_TEXT': "More than {count} items...",
# Schemas
'SCHEMA_COERCE_PATH_PK': True,
'SCHEMA_COERCE_METHOD_NAMES': {
'retrieve': 'read',
'destroy': 'delete'
},
}DEFAULT_RENDERER_CLASSES
渲染的类
'DEFAULT_RENDERER_CLASSES': [
'rest_framework.renderers.JSONRenderer', # 将数据渲染成JSON
'rest_framework.renderers.BrowsableAPIRenderer', # 可浏览的渲染器,\
# 之前用浏览器直接访问时见到的页面,就是该渲染器的作用
]DEFAULT_PARSER_CLASSES
转换数据的类
'DEFAULT_PARSER_CLASSES': [
'rest_framework.parsers.JSONParser', # 转换json
'rest_framework.parsers.FormParser', # 转换表单
'rest_framework.parsers.MultiPartParser' # 文件上传
],DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES
认证
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': [
'rest_framework.authentication.SessionAuthentication', # session认证
'rest_framework.authentication.BasicAuthentication' # 基本认证
],DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES
用于权限管理
'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES': [
'rest_framework.permissions.AllowAny', # 默认允许任何人
],DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES
节流
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES': [], # 节流默认为空DEFAULT_CONTENT_NEGOTIATION_CLASS
文本过滤
# 默认使用DefaultContentNegotiation
'DEFAULT_CONTENT_NEGOTIATION_CLASS': 'rest_framework.negotiation.DefaultContentNegotiation',DEFAULT_METADATA_CLASS
元信息类
'DEFAULT_METADATA_CLASS': 'rest_framework.metadata.SimpleMetadata', # 默认使用此类DEFAULT_VERSIONING_CLASS
版本控制
'DEFAULT_VERSIONING_CLASS': None, # 版本控制其他类介绍
# Generic view behavior
'DEFAULT_PAGINATION_CLASS': None, # 默认分页类
'DEFAULT_FILTER_BACKENDS': [], # 过滤客户端
# Schema
'DEFAULT_SCHEMA_CLASS': 'rest_framework.schemas.openapi.AutoSchema',
# Throttling 节流频率
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES': {
'user': None, # 限制用户
'anon': None,
},其他的以后有空再做解释。
as_view
调用父类中的as_view,并且dispatch重写
@classmethod
def as_view(cls, **initkwargs):
"""
Store the original class on the view function.
This allows us to discover information about the view when we do URL
reverse lookups. Used for breadcrumb generation.
"""
# 如果有queryset,就强行运算
if isinstance(getattr(cls, 'queryset', None), models.query.QuerySet):
def force_evaluation():
raise RuntimeError(
'Do not evaluate the `.queryset` attribute directly, '
'as the result will be cached and reused between requests. '
'Use `.all()` or call `.get_queryset()` instead.'
)
cls.queryset._fetch_all = force_evaluation
view = super().as_view(**initkwargs) # 继承父类的as_view方法
view.cls = cls
view.initkwargs = initkwargs
# Note: session based authentication is explicitly CSRF validated,
# all other authentication is CSRF exempt.
return csrf_exempt(view)并且,在restframework的views中,重写了Django原生views中的dispatch,所以在调用的是APIView中重写的dispatch函数。
所以在重写完dispatch之后,当访问不存在的接口,就不会跳转到django原生的报错页面,而是返回restframework定制的内容。
25行调用了csrf_exempt实行了自动豁免,所以在类视图中,所有的请求直接自动豁免。
重写的dispatch
重写的dispatch:
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
`.dispatch()` is pretty much the same as Django's regular dispatch,
but with extra hooks for startup, finalize, and exception handling.
"""
self.args = args # 记录参数
self.kwargs = kwargs
request = self.initialize_request(request, *args, **kwargs) # 初始化request
self.request = request
self.headers = self.default_response_headers # deprecate?
try:
self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs)
# Get the appropriate handler method (获得适合的处理方法)
if request.method.lower() in self.http_method_names:
handler = getattr(self, request.method.lower(),
self.http_method_not_allowed)
else: # 如果请求不是规定的请求,返回http_method_not_allowed
handler = self.http_method_not_allowed
response = handler(request, *args, **kwargs)
except Exception as exc:
response = self.handle_exception(exc)
self.response = self.finalize_response(request, response, *args, **kwargs)
return self.response- 第8行使用
initialize_request()来初始化request - 第13又使用了
initial()初始化 - 第20行使用了
http_method_not_allowed来表示获得请求类型不被允许 - 24、25两行使用
handle_exception处理抛出的异常 第27行
finalize_response()对response进行加工initialize_request
源码如下:
def initialize_request(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Returns the initial request object.
"""
parser_context = self.get_parser_context(request) # 从原生的request中提取出context
return Request( # 构建新的request
request,
parsers=self.get_parsers(), # 转换器
authenticators=self.get_authenticators(), # 获取认证器
negotiator=self.get_content_negotiator(), # 获取内容过滤器
parser_context=parser_context # 内容
)initial
源码如下:
def initial(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Runs anything that needs to occur prior to calling the method handler.
"""
self.format_kwarg = self.get_format_suffix(**kwargs)
# Perform content negotiation and store the accepted info on the request
neg = self.perform_content_negotiation(request) # 内容检索
request.accepted_renderer, request.accepted_media_type = neg
# 第九行使用元组拆解,将neg拆解成可接受渲染和可接受媒体类型
# Determine the API version, if versioning is in use.(决定版本是否支持)
version, scheme = self.determine_version(request, *args, **kwargs)
request.version, request.versioning_scheme = version, scheme
# Ensure that the incoming request is permitted (确保发送来的请求被允许)
self.perform_authentication(request) # 执行认证
self.check_permissions(request) # 检查权限
self.check_throttles(request) # 检测频率重点在于16-19行对请求的各种检查,如检查登录,检查权限,检测访问频率
perform_authentication
def perform_authentication(self, request):
"""
Perform authentication on the incoming request.
Note that if you override this and simply 'pass', then authentication
will instead be performed lazily, the first time either
`request.user` or `request.auth` is accessed.
"""
request.user # 只调用了一个属性就可以达到检查认证的效果查看这个user属性:
@property # @property 作用是将一个方法改为属性
def user(self):
"""
Returns the user associated with the current request, as authenticated
by the authentication classes provided to the request.
"""
if not hasattr(self, '_user'):
with wrap_attributeerrors():
self._authenticate() # 执行认证操作
return self._user查看self._authenticate() 这个私有方法:
- 可以看出这个函数执行用户认证
遍历认证器
- 如果认证成功返回一个元组
- 元组中的第一个元素就是user
- 第二个元素是auth和token
def _authenticate(self): """ Attempt to authenticate the request using each authentication instance in turn. """ for authenticator in self.authenticators: try: user_auth_tuple = authenticator.authenticate(self) #调用方法 except exceptions.APIException: self._not_authenticated() # 如果出错就返回没有认证 raise if user_auth_tuple is not None: # 如果认证完的元组不为空 self._authenticator = authenticator self.user, self.auth = user_auth_tuple # 验证器元组中存储user和auth return self._not_authenticated() # 如果上述都不执行,还是返回认证失败
check_permissions
- 权限检查
遍历权限检测器
- 只要有一个权限检测未通过,直接显示权限被拒绝
- 所有权限都满足,才被认为拥有权限
源码:
def check_permissions(self, request):
"""
Check if the request should be permitted.
Raises an appropriate exception if the request is not permitted.
"""
for permission in self.get_permissions(): # 遍历权限,只要有一个权限不足就执行下述代码
if not permission.has_permission(request, self): # 如果没有权限
self.permission_denied( # 拒绝
request,
message=getattr(permission, 'message', None),
code=getattr(permission, 'code', None)
)check_throttles
- 检测频率
频率限制器
- 如果验证不通过,就需要等待
def check_throttles(self, request): """ Check if request should be throttled. Raises an appropriate exception if the request is throttled. """ throttle_durations = [] for throttle in self.get_throttles(): if not throttle.allow_request(request, self): # 如果不允许 throttle_durations.append(throttle.wait()) # 进入等待 if throttle_durations: # Filter out `None` values which may happen in case of config / rate # changes, see #1438 durations = [ duration for duration in throttle_durations if duration is not None ] duration = max(durations, default=None) self.throttled(request, duration)
http_method_not_allowed
def http_method_not_allowed(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
If `request.method` does not correspond to a handler method,
determine what kind of exception to raise.
"""
raise exceptions.MethodNotAllowed(request.method)如果请求类型不被允许,就抛出异常MethodNotAllowed
MethodNotAllowed
class MethodNotAllowed(APIException):
status_code = status.HTTP_405_METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED
default_detail = _('Method "{method}" not allowed.') # 默认描述
default_code = 'method_not_allowed'
def __init__(self, method, detail=None, code=None):
if detail is None:
detail = force_str(self.default_detail).format(method=method)
super().__init__(detail, code)handle_exception
这个函数用来处理异常:
def handle_exception(self, exc):
"""
Handle any exception that occurs, by returning an appropriate response,
or re-raising the error.
"""
if isinstance(exc, (exceptions.NotAuthenticated,
exceptions.AuthenticationFailed)):
# WWW-Authenticate header for 401 responses, else coerce to 403
auth_header = self.get_authenticate_header(self.request)
if auth_header:
exc.auth_header = auth_header
else:
exc.status_code = status.HTTP_403_FORBIDDEN
exception_handler = self.get_exception_handler() # 获取处理异常的handler
context = self.get_exception_handler_context()
response = exception_handler(exc, context)
if response is None: # 如果response为空,就生成一个没有捕获到的异常
self.raise_uncaught_exception(exc)
response.exception = True # 提示响应异常
return responsefinalize_response
def finalize_response(self, request, response, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Returns the final response object.
"""
# Make the error obvious if a proper response is not returned
assert isinstance(response, HttpResponseBase), (
'Expected a `Response`, `HttpResponse` or `HttpStreamingResponse` '
'to be returned from the view, but received a `%s`'
% type(response)
)
if isinstance(response, Response): # 如果response是一个实例
if not getattr(request, 'accepted_renderer', None):
neg = self.perform_content_negotiation(request, force=True)
request.accepted_renderer, request.accepted_media_type = neg
response.accepted_renderer = request.accepted_renderer
response.accepted_media_type = request.accepted_media_type
response.renderer_context = self.get_renderer_context()
# Add new vary headers to the response instead of overwriting.
vary_headers = self.headers.pop('Vary', None)
if vary_headers is not None:
patch_vary_headers(response, cc_delim_re.split(vary_headers))
for key, value in self.headers.items():
response[key] = value
return response总结以上,重写的dispatch函数使用Django中的request,重新构建了restframework的Request,可以对Request直接根据用户认证,权限,访问频率限制 进行智能分发处理。
Restframework中的Request
在原生的request基础上,还添加了认证等等功能,之后封装成新的request
查看restframework中的Request部分源码:
class Request:
"""
Wrapper allowing to enhance a standard `HttpRequest` instance.
Kwargs:
- request(HttpRequest). The original request instance.
- parsers(list/tuple). The parsers to use for parsing the
request content.
- authenticators(list/tuple). The authenticators used to try
authenticating the request's user.
"""
def __init__(self, request, parsers=None, authenticators=None,
negotiator=None, parser_context=None):
assert isinstance(request, HttpRequest), (
'The `request` argument must be an instance of '
'`django.http.HttpRequest`, not `{}.{}`.'
.format(request.__class__.__module__, request.__class__.__name__)
)
self._request = request # 原有request变成私有属性
self.parsers = parsers or ()
self.authenticators = authenticators or ()
self.negotiator = negotiator or self._default_negotiator()
self.parser_context = parser_context
self._data = Empty
self._files = Empty
self._full_data = Empty
self._content_type = Empty
self._stream = Empty
if self.parser_context is None:
self.parser_context = {}
self.parser_context['request'] = self
self.parser_context['encoding'] = request.encoding or settings.DEFAULT_CHARSET
force_user = getattr(request, '_force_auth_user', None)
force_token = getattr(request, '_force_auth_token', None)
if force_user is not None or force_token is not None:
forced_auth = ForcedAuthentication(force_user, force_token)
self.authenticators = (forced_auth,)属性和方法
下面研究封装的新request有哪些函数

content_type
传输的内容类型
@property
def content_type(self):
meta = self._request.META
return meta.get('CONTENT_TYPE', meta.get('HTTP_CONTENT_TYPE', ''))stream
@property
def stream(self):
"""
Returns an object that may be used to stream the request content.
"""
if not _hasattr(self, '_stream'):
self._load_stream()
return self._streamquery_params
查询参数,这里实际就是原来的get请求参数
@property
def query_params(self):
"""
More semantically correct name for request.GET.
"""
return self._request.GETdata
数据,同时兼容get、post、patch的参数
@property
def data(self):
if not _hasattr(self, '_full_data'):
self._load_data_and_files()
return self._full_datauser
如果有用户登录,这里可以直接在请求上获取用户
相当于在请求上添加一个属性,用户对象
@property
def user(self):
"""
Returns the user associated with the current request, as authenticated
by the authentication classes provided to the request.
"""
if not hasattr(self, '_user'):
with wrap_attributeerrors():
self._authenticate()
return self._userauth
认证
相当于在请求上添加了一个属性,属性值为token
@property
def auth(self):
"""
Returns any non-user authentication information associated with the
request, such as an authentication token.
"""
if not hasattr(self, '_auth'):
with wrap_attributeerrors():
self._authenticate()
return self._authsuccessful_authenticator
认证成功
@property
def successful_authenticator(self):
"""
Return the instance of the authentication instance class that was used
to authenticate the request, or `None`.
"""
if not hasattr(self, '_authenticator'):
with wrap_attributeerrors():
self._authenticate()
return self._authenticator总结:restframework在django基础上又封装了很多功能。
了解这些对后面学习用户认证,权限管理,频率检测有帮助。
Restframework中的Response
中文文档:https://q1mi.github.io/Django-REST-framework-documentation/tutorial/2-requests-and-responses_zh/
REST框架还引入了一个Response对象,这是一种获取未渲染(unrendered)内容的TemplateResponse类型,并使用内容协商来确定返回给客户端的正确内容类型。
实验:
views.py:
class StudentView(APIView):
def post(self,request):
return Response({'msg':'ok'}, 201)使用poserman测试:

所以使用rest封装的response,可以直接返回json格式数据,并且可以传递状态码参数。
查看封装的Response部分源码:
class Response(SimpleTemplateResponse): # 继承django原生的SimpleTemplateResponse
"""
An HttpResponse that allows its data to be rendered into
arbitrary media types.
"""
def __init__(self, data=None, status=None,
template_name=None, headers=None,
exception=False, content_type=None):
"""
Alters the init arguments slightly.
For example, drop 'template_name', and instead use 'data'.
Setting 'renderer' and 'media_type' will typically be deferred,
For example being set automatically by the `APIView`.
"""
super().__init__(None, status=status)
if isinstance(data, Serializer):
msg = (
'You passed a Serializer instance as data, but '
'probably meant to pass serialized `.data` or '
'`.error`. representation.'
)
raise AssertionError(msg)
self.data = data
self.template_name = template_name
self.exception = exception
self.content_type = content_type
if headers:
for name, value in headers.items():
self[name] = value属性和方法
rendered_content
渲染内容
@property
def rendered_content(self):
renderer = getattr(self, 'accepted_renderer', None)
accepted_media_type = getattr(self, 'accepted_media_type', None) # 获取类型
context = getattr(self, 'renderer_context', None) #获取内容
assert renderer, ".accepted_renderer not set on Response"
assert accepted_media_type, ".accepted_media_type not set on Response"
assert context is not None, ".renderer_context not set on Response"
context['response'] = self
media_type = renderer.media_type
charset = renderer.charset
content_type = self.content_type
if content_type is None and charset is not None:
content_type = "{}; charset={}".format(media_type, charset)
elif content_type is None:
content_type = media_type
self['Content-Type'] = content_type
ret = renderer.render(self.data, accepted_media_type, context) # 进行渲染
if isinstance(ret, str):
assert charset, (
'renderer returned unicode, and did not specify '
'a charset value.'
)
return ret.encode(charset)
if not ret:
del self['Content-Type']
return retstatus_text
将状态码转换成文本
@property
def status_text(self):
"""
Returns reason text corresponding to our HTTP response status code.
Provided for convenience.
"""
return responses.get(self.status_code, '')
此处评论已关闭